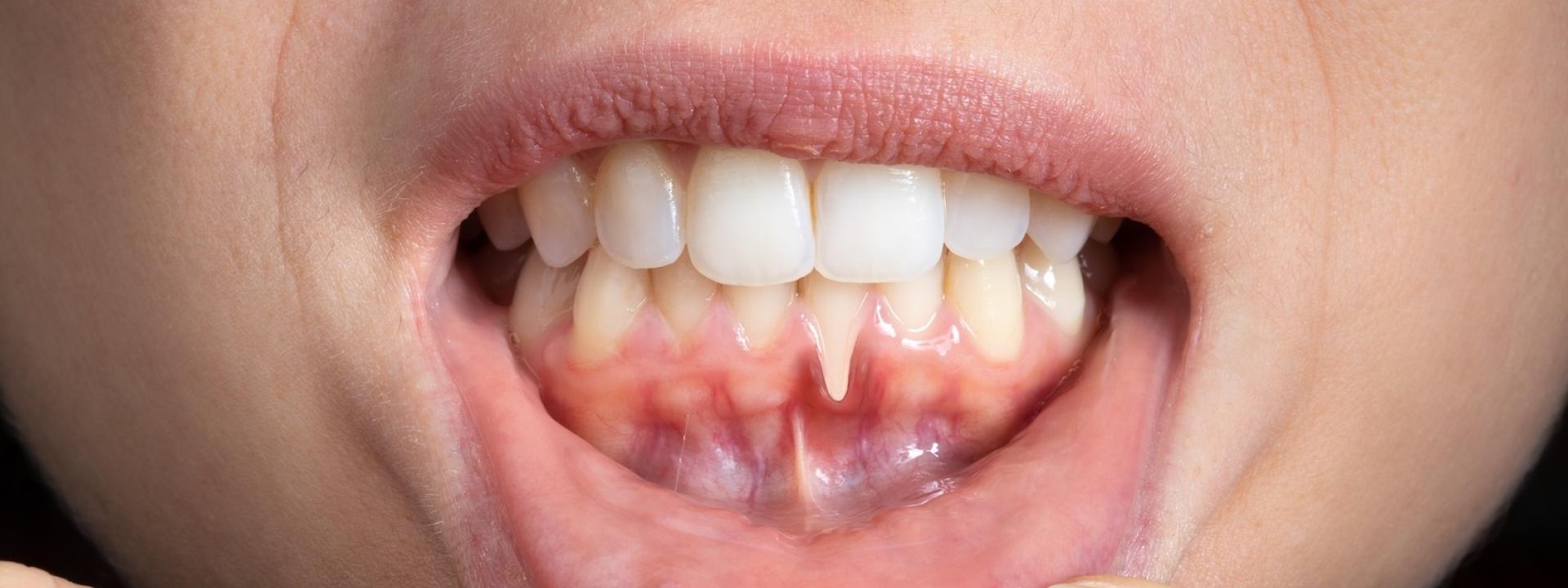
Have you ever noticed your teeth appearing longer or cringed at a cold beverage touching your exposed roots? These could be subtle signs of gum recession, a gradual loss of gum tissue that exposes the sensitive root surfaces underneath. While common, gum recession shouldn’t be taken lightly.
What is the primary cause of gum tissue loss?
The primary culprit behind gum recession often hides in plain sight: plaque. Bacteria form this sticky film so they can stick to teeth and not be washed away by the saliva. If not removed daily through diligent brushing and flossing, it hardens into calculus, a stubborn deposit that clings to the tooth above and below the gum line. Left unchecked, plaque and calculus irritate the gums, triggering a cascade of events that can eventually lead to gum loss.
What are the stages of gum irritation?
1. Gingivitis - characterized by red, inflamed gums that bleed easily. Gingivitis is reversible with good oral hygiene.
2. Periodontitis - if Gingivitis is neglected, a severe infection develops that damages both the gum tissue and the underlying bone supporting your teeth. This can be treated with deep cleanings and coaching on how to maximize your home care.
3. Periodontal disease - if the initial infection is left unchecked it will begin a progressively worsening destruction of the gums, surrounding bone and eventually even the teeth . In some cases this can still be resolved with in depth treatment and follow up care, but in some cases the teeth have to be extracted. We never want you to get to this point!!!
What are other causes of gum tissue loss?
While plaque and gum disease are the leading culprits, other factors can contribute to gum recession. Most are caused by some form of bone loss which leads to a change in position or loss of the overlying gum tissue.
1. Aggressive Brushing - Overzealous scrubbing with a hard-bristled toothbrush can wear away gum tissue and does more harm than good. Opt for gentle brushing with a soft-bristled brush, and focus on removing plaque at the gum line with slow gentle circles of the tooth brush bristles.
2. Clenching and grinding - causes traumatic stress and movement of the teeth leading to traumatic bone loss around the teeth
3. Misaligned teeth - increasingly difficult to clean adequately as teeth become more crowded and misaligned. This starts the cascade of gum irritation. Unresolved this will lead to bone and gum tissue loss.
4. Bad habits - nail biting, etc, that cause excessive forces on the teeth can lead to traumatic bone loss
5. Metal oral objects - tongue studs, lip rings, etc can cause trauma to the nearby tissues. This leads to strong inflammation which leads to bone loss.
6. Diabetes - healing abilities of the tissues are decreased. Gum tissue will become extremely inflamed with even minor failures in cleaning.
7. Tobacco use - Smoking weakens your immune system and decreases blood flow to your gums. This makes them more susceptible to infection and recession. Quitting smoking is crucial for both overall and oral health.
Recognizing the Signs of gum tissue loss
Early detection and treatment are the keys to effectively managing gum recession.
Be mindful of these telltale signs of gum recession:
1. Receding gum line - This exposes more of the tooth root, making teeth appear longer. If you can see more of the surface of a tooth or multiple teeth, your gums are receding.
2. Sensitivity to hot and cold - exposed tooth roots are more sensitive to hot, cold and sweets, so you may experience new or worsening discomfort as your gums recede.
3. Gingival bleeding: Bleeding gums, even during gentle brushing or flossing, indicate there is a problem. Contact your dentist.
4. Loose teeth: Advanced gum recession can loosen teeth, potentially leading to tooth loss.
What are the treatment steps for gum loss?
The good news is that gum recession is treatable, depending on its severity.
1. Stop the gum loss - Deep cleanings with a hygienist will help remove the plaque and calculus from above and below your gumline. As long as you continue to work hard at cleaning your teeth at home EACH DAY, the gum tissue should return to a healthy state. Your dentist may also prescribe antibiotics or medicated mouthwashes to control infection.
2. Coaching and follow up care - your hygienist will help you understand the best cleaning devices (SOFT), techniques and materials to get your teeth sparkling clean each day. You will have follow up appointments to assess your healing and effectiveness of your home cleaning.
3. Fix any defects in the root surfaces - fractures or cavities must be addressed ASAP, especially when they are in the softer root surfaces.
4. Prescription Fluoride toothpaste treatment - used to harden the root surfaces and enamel. This decreases the potential for damage to the softer root surfaces and helps desensitize the roots over time. And yes, used correctly, fluoride is COMPLETELY safe.
5. Gum tissue grafting - if exposed root surfaces are free of cavities or fillings there is the possibility of replacing the missing gum tissue. A periodontist (dental specialist who works with gum tissue and bone) can graft gum tissue from other locations in the mouth to cover the exposed root surfaces.
Preventing gum tissue loss:
The best approach to gum recession is prevention. Here are some important steps to incorporate into your routine:
1 Practice good oral hygiene: Brush and floss twice daily. Use prescription Fluoride toothpaste to harden the teeth and any already exposed roots.
2. Use proper brushing techniques: Avoid aggressive brushing and use a soft-bristled toothbrush to clean gently at the gum line.
3. Schedule regular dental checkups and cleanings: Schedule appointments with your dentist every 6 months for professional cleanings and checkups to detect and address gum problems early on.
4. Kick the tobacco habit: Quitting smoking is essential for improving your overall health and preventing gum disease and recession. Seek support from your doctor or other resources if needed.
5. Manage underlying health conditions: Diabetes and other health issues can impact oral health. Work with your healthcare team to manage them effectively.
6. Consider protective measures: If you grind your teeth, wear a mouthguard while sleeping to prevent damage.
Conclusion
Gum recession is a common concern, but it doesn’t have to dictate your oral health journey. If you experience gum recession, don’t hesitate to make an appointment with your dentist. Together, you can create a personalized plan to address the issue and maintain a healthy, beautiful smile for years to come.
Cheers,
Dr. Appel